Vertical Hoeffding Tree (VHT) classifier is a distributed classifier that utilizes vertical parallelism on top of the Very Fast Decision Tree (VFDT) or Hoeffding Tree classifier.
Very Fast Decision Tree (VFDT) classifier
Hoeffding Tree or VFDT is the standard decision tree algorithm for data stream classification. VFDT uses the Hoeffding bound to decide the minimum number of arriving instances to achieve certain level of confidence in splitting the node. This confidence level determines how close the statistics between the attribute chosen by VFDT and the attribute chosen by decision tree for batch learning.
For a more comprehensive summary of VFDT, read chapter 3 of Data Stream Mining: A Practical Approach.
Vertical Parallelism
Vertical Parallelism is a parallelism approach which partitions the instances in term of attribute for parallel processing. Vertical-parallelism-based decision tree induction processes the partitioned instances (which consists of subset of attribute) to calculate the information-theoretic criteria in parallel. For example, if we have instances with 100 attributes and we partition the instances into 5 portions, we will have 20 attributes per portion. The algorithm processes the 20 attributes in parallel to determine the “local” best attribute to split and combine the parallel computation results to determine the “global” best attribute to split and grow the tree.
For more explanation about available parallelism types for decision tree induction, you can read chapter 4 of Distributed Decision Tree Learning for Mining Big Data Streams, the Developer’s Guide of SAMOA.
Vertical Hoeffding Tree (VHT) classifier
VHT is implemented using the SAMOA API. The diagram below shows the implementation:
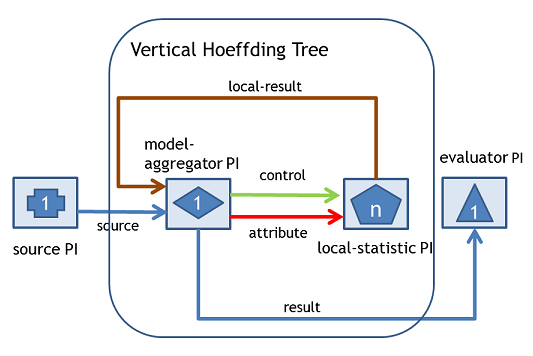
The source Processor and the evaluator Processor are components of the prequential evaluation task in SAMOA. The model-aggregator Processor contains the decision tree model. It connects to local-statistic Processor via attribute stream and control stream. The model-aggregator Processor splits instances based on attribute and each local-statistic Processor contains local statistic for attributes that assigned to it. The model-aggregator Processor sends the split instances via attribute stream and it sends control messages to ask local-statistic Processor to perform computation via control stream. Users configure n, which is the parallelism level of the algorithm. The parallelism level is translated into the number of local-statistic Processors in the algorithm.
The model-aggregator Processor sends the classification result via result stream to the evaluator Processor for the corresponding evaluation task or other destination Processor. The evaluator Processor performs an evaluation of the algorithm showing accuracy and throughput. Incoming instances to the model-aggregator Processor arrive via source stream. The calculation results from local statistic arrive to the model-aggregator Processor via computation-result stream.
For more details about the algorithms (i.e. pseudocode), go to section 4.2 of Distributed Decision Tree Learning for Mining Big Data Streams, the Developer’s Guide of SAMOA.